Diamondium is JCVAP’s internal grading system for moissanite (silicon carbide, SiC) materials used in high-temperature accessories such as terp pearls, terp pillars, and other heat-retention components.
Although all Diamondium is based on silicon carbide, different grades show clear differences in purity, crystal structure, defect density, and thermal performance. These differences directly affect heat transfer efficiency, stability, and long-term durability.
This guide explains how Diamondium Grades A, B, C, and D differ, and how those differences translate into real-world performance.
What Determines a Diamondium Grade?

Diamondium grades are classified based on material quality, not size or shape.
Key factors include:
Crystal purity and uniformity
Internal defects and inclusions
Impurity concentration and color centers
Structural density
Thermal conductivity and heat stability
Higher-grade Diamondium materials feature fewer defects and a more continuous crystal structure, allowing heat to transfer more efficiently and evenly.
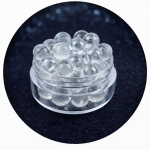
Grade A Diamondium (Highest Grade)

Grade A Diamondium represents the highest purity level within the JCVAP grading system.
Material Characteristics
Fully transparent and crystal-clear appearance
Extremely low defect and impurity levels
Highly uniform single-crystal structure
Thermal Performance
Excellent heat transfer efficiency
Fast and even heat distribution
Estimated thermal conductivity range: ~380–500+ W/m·K
Recommended Use
Premium terp pearls and terp pillars
Daily use and high-temperature sessions
Users seeking maximum consistency and thermal efficiency
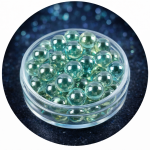
Grade B Diamondium (Colored Single Crystal)
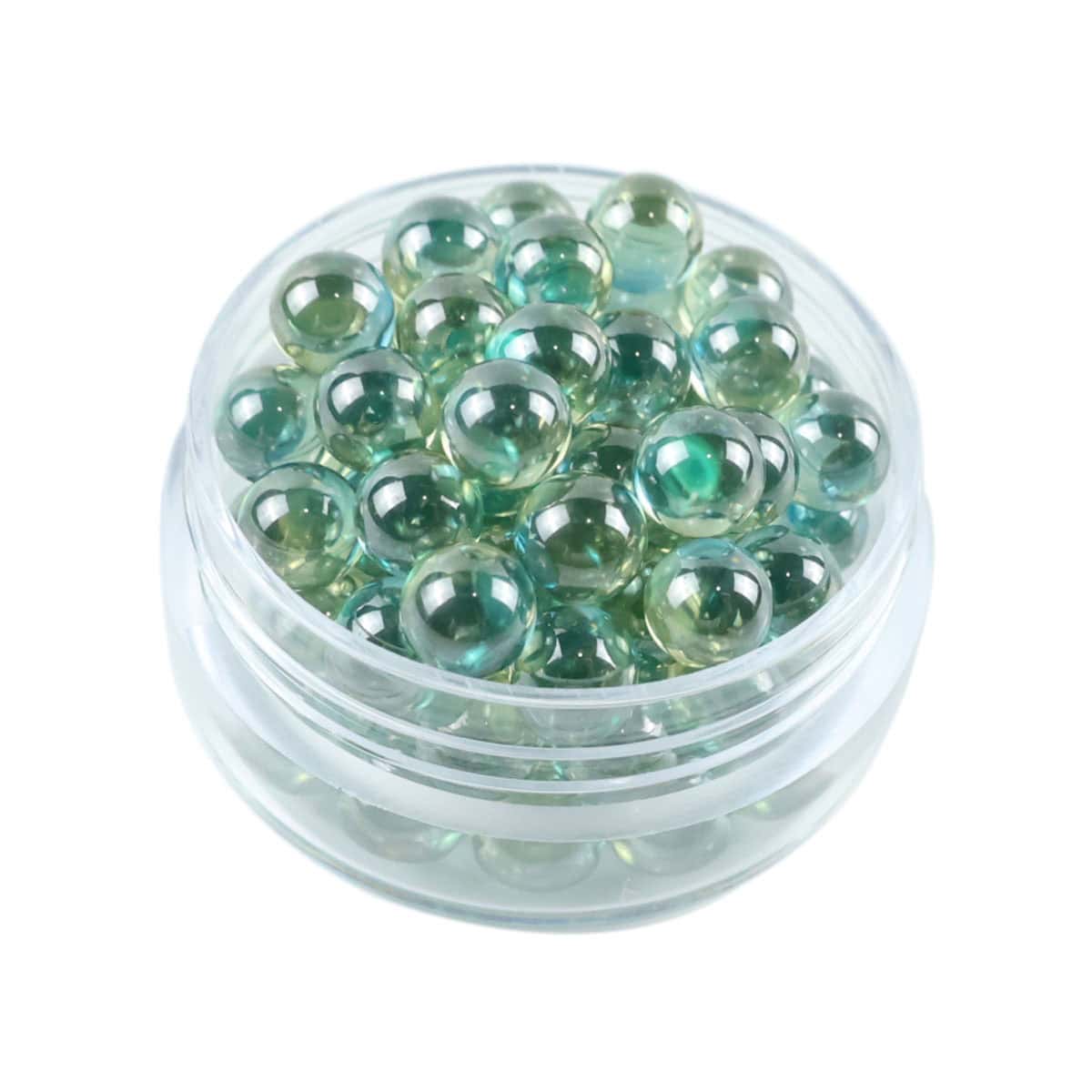

Grade B Diamondium contains controlled impurities or color centers, typically appearing green or champagne in color.
Material Characteristics
Visible coloration caused by trace impurities
Slightly higher defect density than Grade A
Maintains a single-crystal structure
Thermal Performance
Strong and reliable heat transfer
Slightly more variance compared to Grade A
Estimated thermal conductivity range: ~300–420 W/m·K
Recommended Use
Performance-focused users
Users who want both strong thermal behavior and unique aesthetics
Grade C Diamondium (Not Offered)
Grade C Diamondium is not currently offered by JCVAP.
This grade would typically fall between Grade B and Grade D in terms of purity and consistency, but it does not meet JCVAP’s standards for performance stability or material control.
Grade D Diamondium (Mechanical Grade)
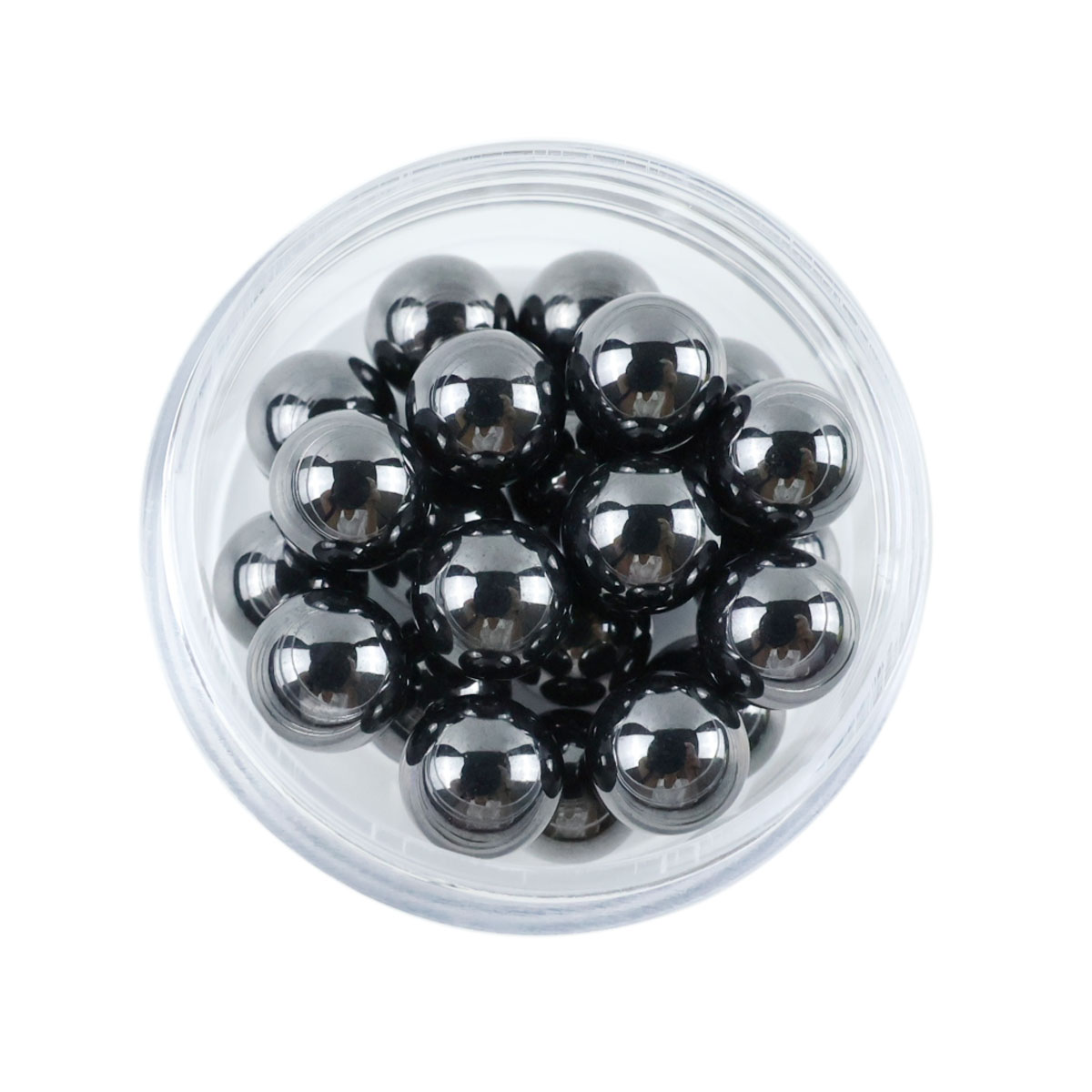

Grade D Diamondium is classified as mechanical-grade silicon carbide. It usually appears black or dark in color and may be slightly translucent.
It is important to clarify that mechanical grade does not mean low performance.
Material Characteristics
High structural density
Higher defect concentration than A or B
Dark or black appearance
Thermal Performance
Significantly higher thermal conductivity than common industrial SiC ceramics
Maintains efficient heat transfer despite increased defects
Estimated thermal conductivity range: ~200–280+ W/m·K
Recommended Use
Reliable functional setups
Cost-efficient configurations
Users prioritizing durability and value over optical clarity
Diamondium Grade Comparison Table
| Grade | Appearance | Structure | Estimated Thermal Conductivity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grade A | Clear / Transparent | High-purity single crystal | 380–500+ W/m·K |
| Grade B | Green / Champagne | Single crystal with color centers | 300–420 W/m·K |
| Grade C | Not offered | — | — |
| Grade D | Black / Slightly translucent | High-density mechanical grade SiC | 200–280+ W/m·K |
How Diamondium Grades Affect Real-World Performance
Heat Response
Higher-grade Diamondium heats faster and distributes energy more evenly across the surface.
Temperature Stability
Lower defect density reduces hot spots and minimizes temperature fluctuation during repeated heat cycles.
Longevity
Premium grades resist clouding, micro-fractures, and surface degradation, maintaining consistent performance over time.
Final Thoughts on Diamondium Grades
Diamondium grading is functional rather than cosmetic.
Even Grade D Diamondium remains a high-performance silicon carbide material, while Grade A and Grade B deliver the highest level of thermal efficiency, stability, and consistency.
Understanding these differences helps users choose the right balance between performance, aesthetics, and cost.
Recommended Products:
-
10% OFF
$18.77 – $41.00Price range: $18.77 through $41.00$16.89 – $36.90Price range: $16.89 through $36.90Diamondium Grade A Terp Pearls 3mm with Titanium Jar
(5)Rated 5.00 out of 5 based on 5 customer ratings -
10% OFF
$10.90 – $20.37Price range: $10.90 through $20.37$9.81 – $18.33Price range: $9.81 through $18.33Diamondium Pearls Grade B 3mm
(2)Rated 5.00 out of 5 based on 2 customer ratings - 10% OFF
-
10% OFF
$999.00Original price was: $999.00.$899.10Current price is: $899.10.Diamondium Grade A XXL Insert for ICA 5D XXL Chamber Custom order only
(0)Rated 0 out of 5